Abstract
The introduction of next generation sequencing has exponentially increased the number of potential disease targets from a limited panel of probes to markers across the entire genome. Previous studies of NGS data in multiple myeloma have identified key features associated with outcome in additive models, typically showing involvement of TP53, gain of 1q, MYC translocations, and others.
We modified the multi-factor dimensionality reduction method (MDR) method, a computationally efficient method for detecting non-linear patterns of gene-gene interactions in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) first proposed by Richie et al, to identify three-way interactions significantly associated with outcome in MM. Specifically, we altered the ranking strategy of the survival adapted Cox-MDR method of Lee et al from balanced accuracy (average of sensitivity and specificity) to the absolute sum of deviance residuals. Due to the high level of censoring (94 events in 559 cases), balanced accuracy ranking favored interactions that identified few high risk cases and failed to validate well on external data.
The publically available MMRF CoMMpass trial database (release version IA10) was utilized as primary training set for our MDR method. We included in our comparisons 164 RNA-SEQ genes with significant association with overall survival, the 20 most abundant non-synonymous, non-IG variants, and 24 estimated whole chromosome arm copy number gains or loss calls from the long insert WGS data of 559 baseline cases with outcome and clinical data (median follow-up 1.8 years). We searched for all three-way interactions across 210 total features resulting in the ranking of over 1.5 million unique three-way interactions, adjusted for age, ISS, creatinine level, and treatment by modified MDR. The top three-way RNA-expression interactions from our discovery phase were validated on 540 cases with GEP microarray and clinical data from UAMS Total Therapy 2 and 3 with median follow-up of 4.66 years (publically available data from GSE2658, GSE31161, and GSE24080).
Of the top 100 three-way gene expression interactions discovered that we could validate on Affymetrix GEP data, 84 were significant in the UAMS TT2 and TT3 data set (log rank p-value < 0.05). HMGB3, a proposed inhibitor of myeloid differentiation, and DDX51, known to be differentially methylated in ALL, were the most commonly involved genes in the top significant interactions across both data sets. Pathway analysis of the 150 most frequently observed genes across the top 5,000 interactions in CoMMpass revealed an enrichment of DNA replication and cell cycle associated genes: RFC5, MCM2, MCM3, MCM4, MCM6, CCNA2, CDK2, etc.
Within the top interactions that included whole arm copy number variants, gain of 1q and loss of 13q were the most frequently observed. We note that the top three-way interactions with gain of 1q paired exclusively with ALYREF, a transcriptional promoter, and one additional gene. Of the top interactions that included a SNV, mutations of DIS3 and DNAH5 were the most frequently observed. Many of the top interactions including DIS3 mutations paired with HMGB3 or TRIB3, a negative regulator of NF-kB and sensitizer to apoptosis, and one additional gene.
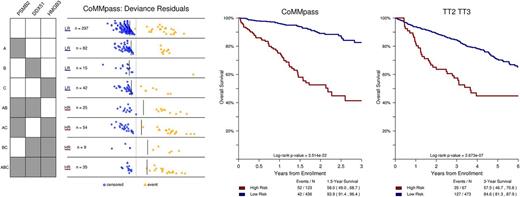
MDR models are capable of identifying complex interactions of features that are not strictly additive. We observed a variety of interaction models, and present below an example where presence of 2 or more features resulted in overall negative outcome while presence of 1 or fewer did not. This situation was observed for the interaction of high expression of HMGB3, DDX51, and PSMB2, a bortezomib sensitizer in MM cell lines, where high expression in 2 or more of these genes imparted a negative outcome in CoMMpass and TT2/TT3 data sets. In the TT2/TT3 data set, cases identified as high risk from this interaction were enriched for the PR subtype and GEP70 HR.
This modified MDR method is an effective tool at mining large genomic data sets for all k -way interactions associated with outcome among binary or multi-level features, adjusted for clinical covariates. Our modifications to MDR method allow us to identify more relevant interactions and increase reliability in validation data. This method could potentially further knowledge of the complex relationships between key features in genomic landscape of MM by discovering novel interactions that identify high-risk phenotypes.
Bergsagel: Phosplatin Therapeutics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal